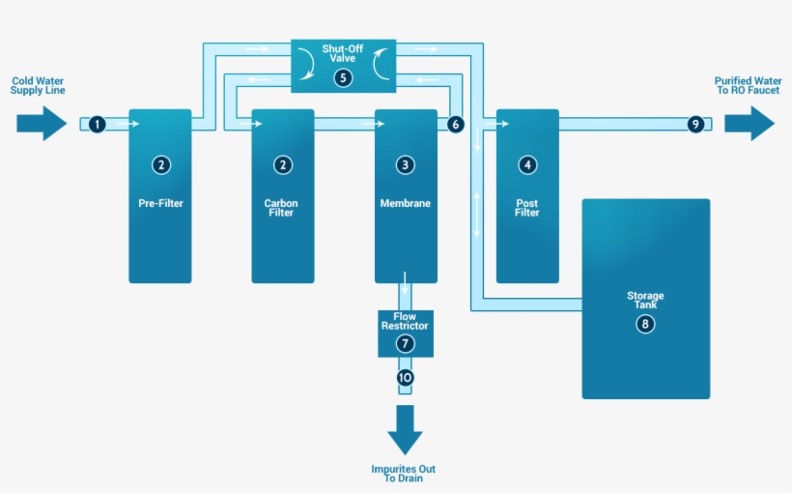
What is reverse osmosis filtration?
Unlike activated carbon filtration technology that uses certain materials to attract contaminants that bind like magnets, reverse osmosis uses a semi-permeable membrane for filtration. Think of it like a mosquito net. Reverse osmosis forces water through a semipermeable membrane, leaving all particles larger than the net behind. But phrasing it like that does reverse osmosis an injustice; it’s more than just forcing water through a net. It uses a considerable amount of water pressure, making it the most effective water purification technique on the market.